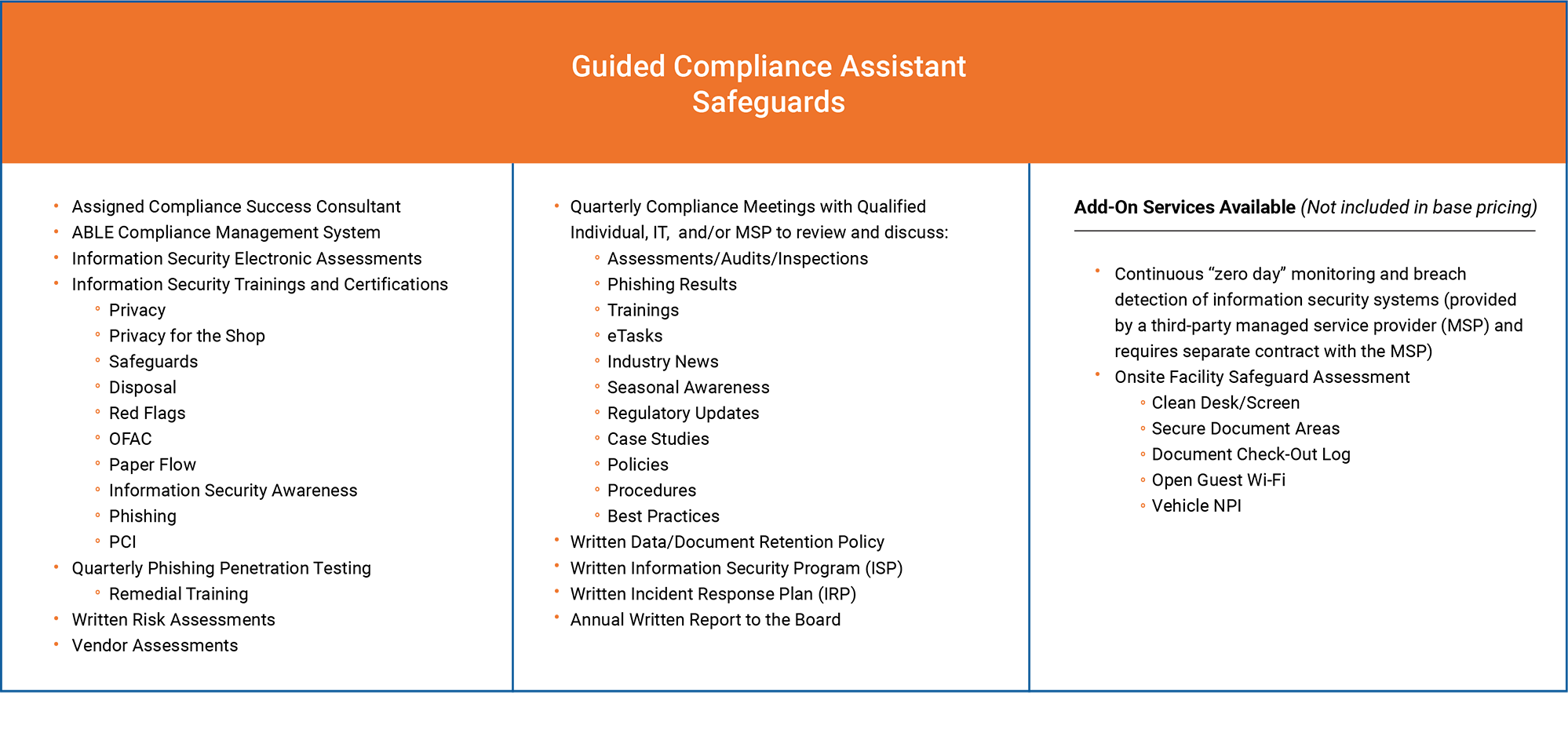
FTC Safeguards Rule
700Credit can help prepare your dealership for these compliance requirements
The Federal Trade Commission (FTC) has finalized changes to the Standards for Safeguarding Customer Information rule (Safeguards Rule) under the Gramm-Leach-Bliley Act (GLBA). The updated Safeguards Rule amends the FTC’s 2003 Safeguards Rule and requires financial institutions (which includes Dealers) to strengthen their data security safeguards to protect customer financial information.
Please fill out the form to keep your staff properly trained in FTC Safeguards requirements. A 700Credit Representative will be in contact with you shortly
Watch our educational webinar series on the New FTC Safeguard Rules
Part 1:
Gain a high level understanding of what the new Safeguards Rule includes and what it means for your dealership. Just getting started? Start here.
Part 2:
You understand what is included in the new Safeguards Rule, now we will talk about how to tackle each aspect of implementing it in your dealership.
Part 3:
The deadline is extended to June 9th, 2023, but certain provisions are still required to be in place by December ’22. Learn what’s changed, and what hasn’t.
How this affects your dealership
The updated Safeguards Rule now includes specific criteria for what safeguards financial institutions must implement as part of their information security program. Previously, similar rules provided only general guidance and not specific requirements.
Among other requirements, the updated Safeguards Rule mandates the following:
Designation of Qualified Individual: | Designate a qualified individual to be responsible for the information security program. |
Written Information Security Program: | Establish a comprehensive written information security program, including designating a qualified individual for overseeing and implementing the program. |
Risk Assessments: | Undertake risk assessments and implement safeguards to address identified risks. Assessments must be in writing and include criteria for evaluating and identifying security risks, as well as ways to mitigate or accept those risks. Risk assessments must be performed periodically to reassess the reasonably foreseeable risks to the security of customer information. |
Penetration Tests and Vulnerability Assessments: | Annual penetration tests of information systems. Vulnerability assessments, including any system scans or reviews of information systems, must be completed every 6 months. |
Encryption of Customer Information at Rest and in Transit: | Encrypt all customer information, both in transit over external networks and at rest. |
Service Provider Oversight: | Take reasonable steps to select and retain third-party service providers that maintain appropriate safeguards for customer information and periodically assess service providers to ensure compliance. |
Additional Training Requirements: | Update the training for employees based upon risk assessments and/or changes in practices and verify that training requirements have been met. |
Multifactor Authentication: | Implement multifactor authentication for individuals accessing networks that contain customer information. Authentication measures may include (1) knowledge factors (a password); (2) possession factors (a token); or (3) inherence factors (biometric characteristics). |
Logging and Disposal of Customer Information: | Develop, implement, and maintain procedures for the secure disposal of customer information no later than 2 years after the last date the information was used, unless otherwise required to retain the information longer, and implement policies, procedures and controls designed to monitor and log the activity of unauthorized users and detect unauthorized access, use or tampering with customer information. |
Reports to Board of Directors: | The qualified individual must provide written reports at least annually to boards of directors or governing bodies on the financial institution’s information security program. Including information on the overall status of the information security program and the financial institution’s compliance, and material matters related to the information security program (such as risk assessments and recommended updates to the program). |